
Depending on the stage of charging the battery has reached, contemporary battery chargers modify the charging conditions dynamically. Without any safety concerns, a dead battery can be charged more quickly. Due to this, most benchmarks for charging speed, including our own, list the battery charging level attained following a 30-minute charging session on an empty battery.
Anything that charges more quickly is referred to as quick or fast charging because basic chargers only provide 5V/1A, which is equal to 5W of power.
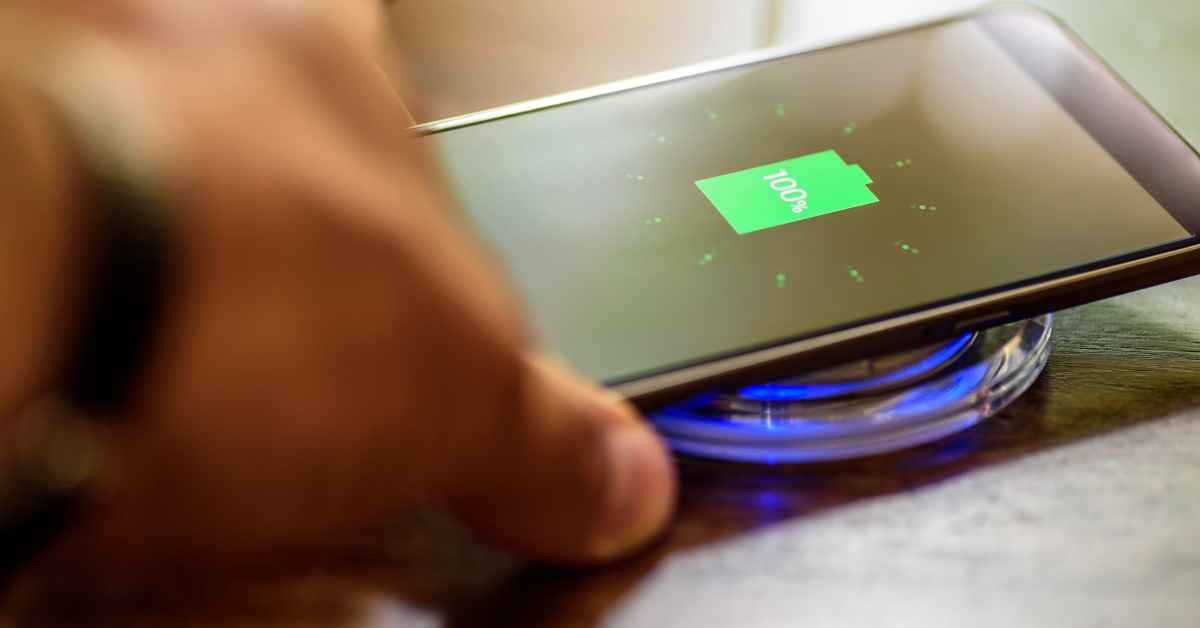
Wireless charging
Using an electromagnetic field, wireless (or inductive) charging transfers energy between two items via electromagnetic induction. To use induction, simply place a device with an induction coil directly onto a special charging station.
In the past, there were at least a few wireless charging protocols that were in competition with one another, but today the entire mobile industry uses Qi.
Wireless charging can be done at various rates, just like with conventional wired charging. A Qi charging pad’s maximum power output is 5W, while faster chargers can currently deliver up to 15W to compatible phones.
Quick charging
The quick charging market is still incredibly fragmented, and nearly every manufacturer has its own solution—often using proprietary technology.
The most popular option is 5V/2A charging, which provides 10W of power and is supported by virtually all other phones. From there and upward, the charging gets really quick.
The QuickCharge protocol from Qualcomm is compatible with smartphones using Qualcomm chipsets. It has undergone several iterations, the most recent being QuickCharge 4+.
The most widespread implementations have a peak power output of 18W and are backward compatible with earlier generations. Even though Motorola markets their phones as having TurboPower and makes no mention of QuickCharge, they nonetheless adhere to this standard.
Comparable to Snapdragon, MediaTek has also unveiled Pump Express, a proprietary charging standard that only works with specific phones that use the company’s chipsets.
PumpExpress 3.0, the most recent version of the standard, has a USB-C connector for the charging cord. It is possible to use a micro USB port with Pump Express+ 2.0, which also offers a more affordable option.
Another quick charging method that is not specific to one piece of hardware is USB Power Delivery. It does need a USB-C to USB-C cable, but it doesn’t need any proprietary hardware.
There are also laptops that employ this standard for charging, so the maximum power output is 100W. However, current smartphone implementations can only output 18W of electricity.
Because Oppo, Vivo, and OnePlus share certain intellectual property and R&D, their phones use comparable quick charging technologies.
Oppo refers to it as VOOC Flash charge, Vivo refers to it simply as Fast battery charging, and OnePlus previously referred to it as Dash charge. The three models all produce 18–20W of power.









[…] Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE): Also known as Bluetooth Smart, this version of Bluetooth is designed for low-power devices such as sensors, wearables, and other IoT devices. It consumes less energy than Classic Bluetooth and can maintain a connection for months or even years on a single battery charge. […]